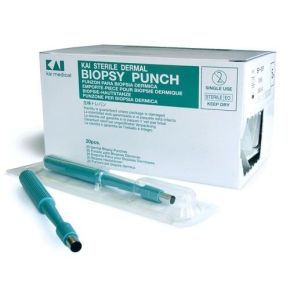
Skin Biopsy Punch
18/11/2024 59
18/11/2024 48
18/11/2024 71
18/11/2024 57
18/11/2024 63
18/11/2024 53
18/11/2024 54
18/11/2024 56
18/11/2024 61
18/11/2024 62
18/11/2024 53
18/11/2024 56
Punch Biopsy: Precise Skin Diagnosis
The punch biopsy is a simple yet powerful medical instrument. In dermatology and pathology, it is used to collect small pieces of skin. These samples allow for the examination of tissues under a microscope, helping doctors accurately diagnose numerous skin diseases. Understanding when to use a punch biopsy, how to choose its size, and how to use it safely is essential for healthcare professionals. This tool plays a significant role in the effective management of skin conditions.
When is it indicated to use a punch biopsy?
The punch biopsy is a versatile tool used in many situations where an accurate diagnosis is necessary. Here are some common cases where its use is indicated:
- Suspicious Skin Cancer Lesions: If a mole changes shape, color, or size, it may be suspicious. The punch biopsy allows for the collection of a sample to check if it is a melanoma or another type of skin cancer.
- Inflammatory Skin Diseases: Conditions like psoriasis, eczema, or lichen planus may require a biopsy to confirm the diagnosis and guide treatment.
- Deep Skin Infections: When infections do not respond to usual treatments, a biopsy can help identify the responsible pathogen.
- Atypical Pigmented Lesions: Some spots on the skin can be difficult to diagnose visually. The biopsy helps determine their exact nature.
- Bullous Diseases: These diseases cause blisters on the skin. The biopsy helps identify the precise type to choose the correct treatment.
- Unknown Rashes: Sometimes, a rash appears without an obvious cause. The biopsy can help uncover its origin.
In summary, this device is used whenever a detailed examination of skin tissue is necessary for an accurate diagnosis. It is an indispensable tool for dermatologists and pathologists.
What are the different types of punch biopsies?
These essential medical tools in diagnosing dermatological conditions come in various sizes and types, tailored to diverse clinical needs.
Circular Blade Punch
This tool is equipped with a sharp circular blade at its end. It is used to collect samples of cutaneous or mucosal tissues. The blade diameter can vary depending on the required sample size.
Oval Blade Punch
This type of dermatological sampling instrument has an oval-shaped blade at its end. It is often used to collect skin samples during dermatological biopsies. The oval shape allows for a larger sample, which can be useful for analyzing certain skin conditions.
Crescent-Shaped Blade Punch
This skin biopsy instrument has a crescent-shaped blade at its end. It is generally used to collect tissue samples from specific anatomical areas, such as the face or eyelids, where precision and the specific shape of the sample are important.
Needle Punch
This is a tool similar to a hollow needle with a spring-loaded sampling mechanism. It is often used for biopsies of soft tissues, such as breast tissue. The needle is inserted into the target area, and the sample is collected by aspirating the tissue inside the needle.
Aspiration Punch
This type combines a circular cutting blade with an aspiration system. It allows for simultaneous sample collection and tissue suction. It is often used for biopsies of breast tissues or internal organs.
How to choose the appropriate size of the punch biopsy?
Choosing the right size of the punch biopsy is important to obtain an adequate sample while minimizing scarring. Punches are available in different sizes, usually ranging from 2 mm to 8 mm in diameter. Here's how to make the right choice:
- Lesion Size: For a small lesion, a 2 to 3 mm punch is sufficient. This minimizes scarring. For a larger lesion, a 4 to 6 mm punch is preferable to obtain enough tissue.
- Anatomical Site: On the face or sensitive areas, a smaller punch is recommended to reduce visible scarring. On the back or legs, a larger punch can be used without major aesthetic issues.
- Lesion Depth: For deep lesions, a larger diameter punch may be necessary to reach the appropriate tissue layer.
- Diagnostic Purpose: If a detailed analysis is needed, a larger sample can provide more information to pathologists.
- Patient Comfort: A smaller punch is less invasive and heals faster, which may be preferable for some patients.
It is important to balance the need for a sufficiently sized sample with the desire to minimize scarring and complications for the patient. The choice should be tailored to each specific situation.
What are the key steps to perform a punch biopsy safely?
Performing a punch biopsy must be done carefully to ensure patient safety and sample quality. Here are the key steps to follow:
- Patient Preparation: Explain the procedure, obtain informed consent, and review medical history, including allergies and anticoagulant use.
- Antisepsis: Thoroughly clean the area with an appropriate antiseptic to prevent infections.
- Local Anesthesia: Inject a local anesthetic to numb the area and ensure patient comfort during the procedure.
- Performing the Punch: Place the punch perpendicular to the skin and apply a rotational pressure to penetrate the skin layers down to the subcutaneous fat.
- Sample Extraction: Use fine forceps to gently remove the biopsied tissue without damaging it.
- Hemostasis: Apply pressure or use hemostatic agents to control bleeding.
- Suturing if Necessary: Close the site with one or two stitches to promote proper healing, especially for punches larger than 3 mm.
- Sample Labeling: Place the sample in an appropriate container with the necessary information for laboratory analysis.
- Documentation: Record the procedure details in the patient's file, including the site, punch size, and any relevant observations.
By following these steps, the healthcare professional minimizes the risk of complications and ensures the quality of the sample for an accurate diagnosis. Patient safety is always the top priority.
How to manage post-procedure care after a punch biopsy?
After the biopsy, it is important to provide the patient with clear instructions to promote proper healing and prevent infections. Here are the post-procedure care tips:
- Wound Cleaning: The patient should gently clean the area with warm water and a mild soap, avoiding scrubbing.
- Application of Antibiotic Ointment: This helps prevent infections. Apply a thin layer to the wound as recommended by the doctor.
- Changing the Dressing: The dressing should be changed daily or as needed, using a clean and dry dressing.
- Avoid Swimming: It is advised to avoid pools, hot baths, and the sea until complete healing to prevent infections.
- Monitoring for Signs of Infection: The patient should watch the wound for any signs of redness, swelling, pain, or unusual discharge.
- Physical Activities: Avoid intense activities that could reopen the wound, especially if it is located on a mobile area.
- Sun Protection: After healing, it is recommended to protect the area from the sun to prevent hyperpigmented scars.
- Suture Removal: Schedule a follow-up visit to remove stitches, usually between 5 and 14 days depending on the location.
Proper post-procedure care promotes quick healing and reduces the risk of visible scars or infections. The patient should carefully follow the instructions to ensure the best possible outcome.
What are the risks associated with punch biopsy and how to minimize them?
Like any medical procedure, punch biopsy carries certain risks. It is important to be aware of them to effectively minimize them. The main risks include:
- Bleeding: Light bleeding is normal. To minimize it, pressure is applied after the procedure. Patients taking anticoagulants should inform the doctor.
- Infection: Rare, it can be avoided by following care instructions. If signs of infection appear, it is important to consult a doctor promptly.
- Pain: Mild pain may be felt after the procedure. It is generally well controlled with over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen.
- Scar: Any incision leaves a scar. To minimize it, appropriate suturing techniques are used, and scar creams may be recommended.
- Allergic Reactions: Very rare, they can occur with the anesthetic or materials used. It is essential to inform the doctor of any known allergies.
- Nerve Injury: Exceptional, it can occur if a superficial nerve is touched. Choosing the site and using correct techniques minimize this risk.
By informing the patient of the risks and taking precautions, the doctor ensures a safe procedure. Communication and preparation are key elements in reducing potential complications.
In conclusion, the punch biopsy is an indispensable tool for healthcare professionals involved in diagnosing skin conditions. Its use allows for the collection of precise tissue samples, leading to reliable diagnoses. Choosing the appropriate punch size, mastering sampling techniques, and managing post-procedure care are key factors for the success of this intervention. By being aware of the risks and adopting measures to minimize them, practitioners can provide high-quality care to their patients. At Placemed, we offer a comprehensive range of punch biopsies suited to all clinical needs, ensuring quality and safety for your medical practices.
 Francais
Francais